SEO and gendering: Two topics that don’t necessarily go together at first glance. However, in times of digitalisation and change, it is more important than ever that web content is not only optimised for search engines, but also uses language that promotes inclusivity and equality. The gendering of texts is playing an increasingly important role in addressing all people and supporting an inclusive society.
Why use gender-inclusive language?
Gendering is not just a question of political correctness, but also of fairness and equality. By consciously including all genders in our communication, we promote a culture of recognition and respect. Gendering helps to break down stereotypical notions of gender roles and contributes to a society in which every person feels represented and valued.
The challenge of the gender ranking gap in SEO
For marketing experts, gender poses a particular challenge, especially in the context of search engine optimisation (SEO). As the use of gender-sensitive language is not yet mainstream, many people tend to use traditionally “male” terms when searching on Google. For example, “dermatologist” is searched for more often than “female dermatologist”. As a result, websites that use exclusively male terms often perform better in search results than those that use gender-neutral language or female terms. The consequence: If a page is found less frequently, it also receives a lower ranking.
Observations on the gender ranking gap
To illustrate this effect, we made a comparison with the German terms “Hausarzt”, “Hausärztin” and “Hausärzt:in” (as the differences between female and male terms are more clearly recognisable there):
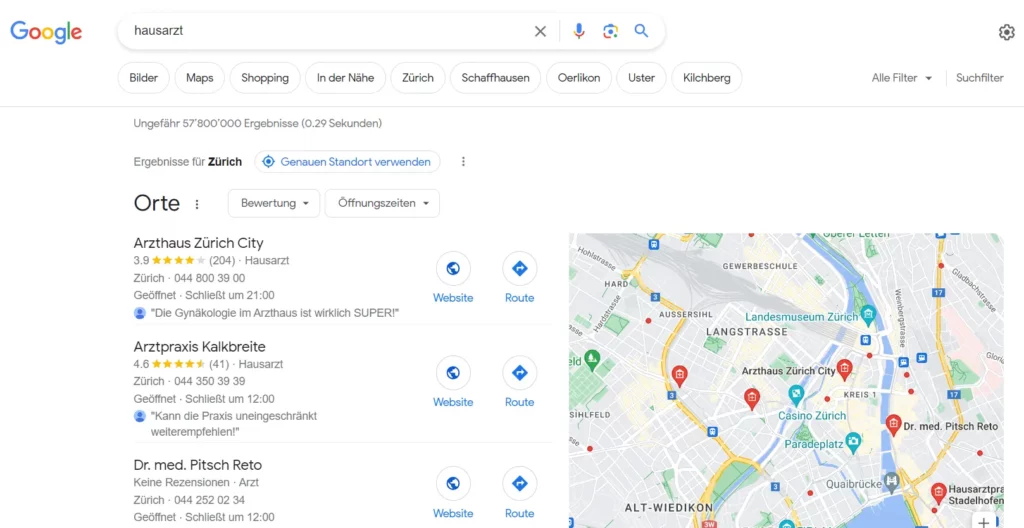
When searching for “Hausarzt”, Google returns 57,800,000 results, with the search engine also displaying local results based on IP address.
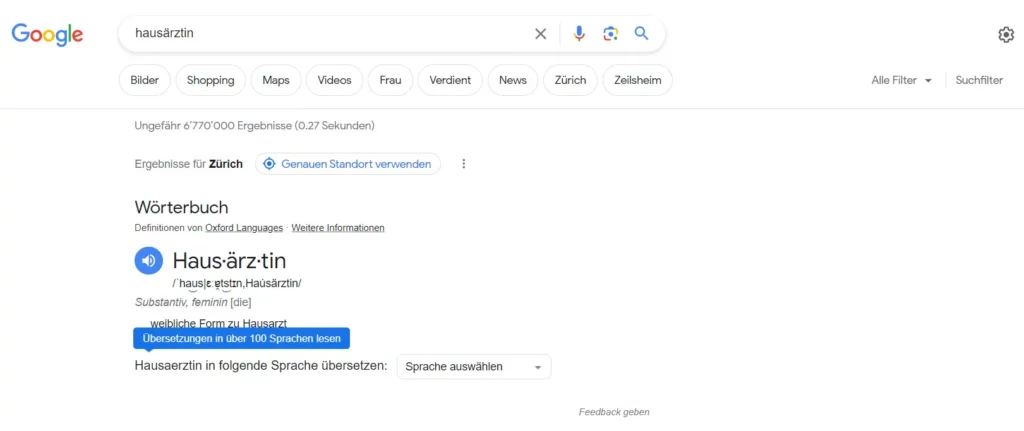
The search for “Hausärztin” results in significantly fewer hits, namely 6,770,000, although Google also takes local relevance into account here.
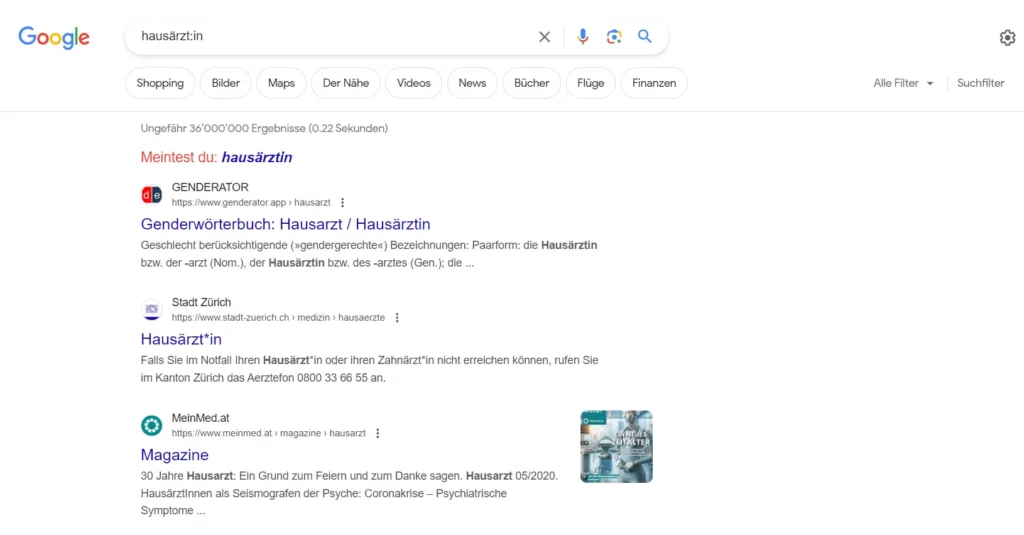
For “Hausärzt:in”, Google shows 36,000,000 results, but without local suggestions and with an attempt to correct the search term.
These differences in search results reflect our search habits. As the majority of users do not search in a gender-inclusive way, websites with feminine or gender-neutral wording are penalised in search results. Although there are numerous ways to use gender-inclusive language today, this is not yet reflected in the search algorithms that significantly influence our online behaviour and information gathering.
These observations highlight the importance of raising awareness and promoting the use of gender-sensitive language not only in everyday communication, but also in digital marketing and SEO to create a more inclusive and equitable digital world. There are many different ways to use gender-sensitive language.
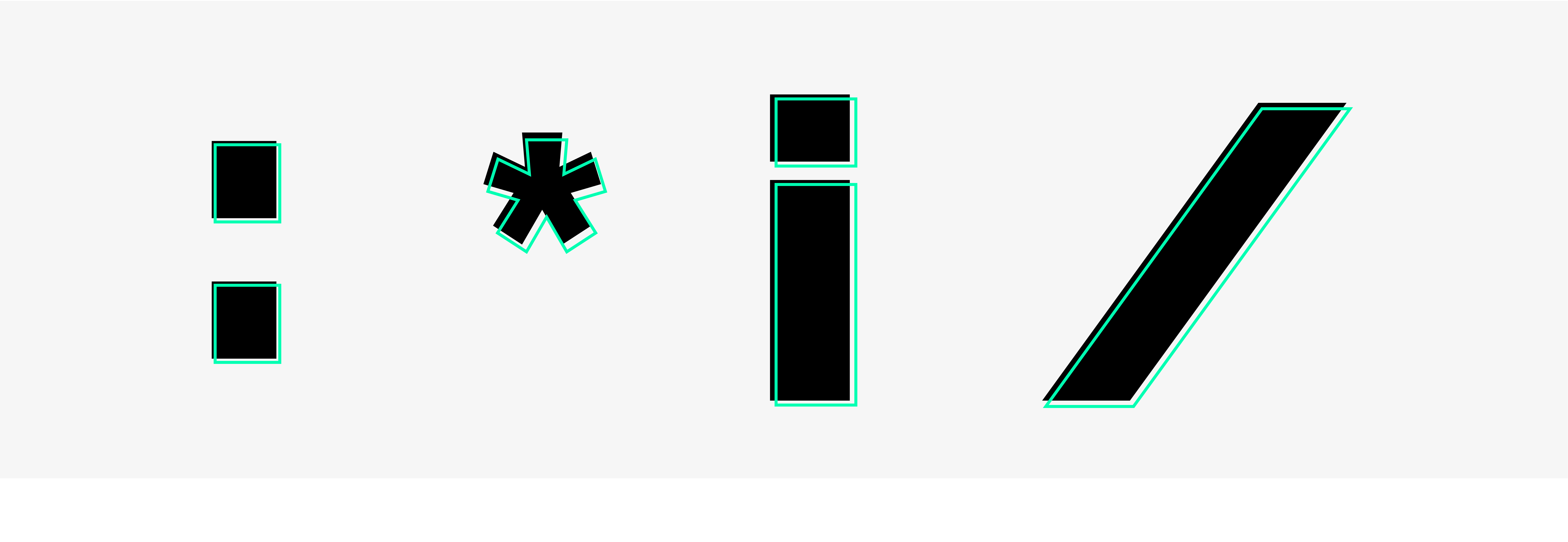
Different gender variants in German
- Paired form: “Mitarbeiter und Mitarbeiterinnen”
- Binnen-I: “MitarbeiterInnen”
- Gender asterisk: “Mitarbeiter*innen”
- Gender colon: “Mitarbeiter:innen”
- Gender gap: “Mitarbeiter_innen”
- Slash: “Mitarbeiter/in” or “Mitarbeiter/-in”
How does Google deal with gender-inclusive language?
Integrating gender-inclusive language into texts is an important way to promote inclusivity without neglecting search engine optimisation. The way you use gender can influence the visibility of your content in Google search results.
Different gender variants and their SEO impact
Gender asterisk and colon: Google often interprets the gender asterisk (*) and colon (:) as spaces. As a result, the terms are perceived separately, for example “Elektriker” and “in”. This can lead to broader coverage in the search results, as both parts of the term are recorded separately.
Underscore (_): Google’s handling of the underscore in gender-appropriate terms is not standardised. In many cases, the term is perceived as a feminine form.
Binnen-I: As Google ignores upper and lower case in search queries, only the female form is usually recognised in such cases. As a result, search results primarily show content with the feminine form.
Paired form: The use of the paired form leads to different results on Google. Sometimes the search engine offers explanations of both forms of a job description, in other cases it tends to automatically correct to the masculine form.
Observations for specific search queries
The search results for masculine and gendered forms can vary greatly. A search for “Elektriker*in” primarily brings up job descriptions, while a search for “Elektriker” tends to return company entries. This illustrates how the choice of gender variant can influence the type of results displayed.
The decision on how to genderise texts has a relevant impact on the findability in Google search results. It is important to be aware of these effects and to adjust the chosen gender strategy if necessary in order to maximise the visibility and reach of the content.
Effective use of gender-inclusive language in texts for better rankings
In order to implement gender-sensitive language in your texts and at the same time achieve a good ranking on Google, you and your team should define a consistent spelling for all forms of communication. The main focus here is that you write primarily for your target group and not exclusively for search engines.
Strategies for gender-appropriate language and SEO
Define standardised spelling: Determine which form of gender you want to use in your internal and external communication. The decision should be made independently of search engine optimisation in order to maintain authenticity and consistency.
Use gender-neutral formulations: Instead of using specific gender forms, you can use gender-neutral terms, such as “Kundschaft”, “Mitarbeitende” or “Teammitglieder”. Such terms focus on the role or function rather than the gender. For example, “web design” or “content creation” can be used instead of “web designer” or “copywriter”. By using gender-neutral terms, you also contribute to the inclusion of non-binary people who do not identify exclusively as male or female.
Use relative clauses: Avoid gender-specific wording by using relative clauses, e.g. “All those who have registered for the webinar…” or “Those who register for the webinar will receive the whitepaper”. This allows you to directly avoid gender-specific language.
Adaptation to the target group: The acceptance of different gender variants can vary depending on the sector and target group. While the gender asterisk is common in some sectors, it may be considered unusual in others.
Utilise resources: The online dictionary geschicktgendern.de offers a variety of gender-neutral alternatives and can serve as a useful resource to make your texts more inclusive. ChatGPT can also help suggest gender-neutral forms for terms.
The deliberate use of gender-inclusive language combined with strategic SEO allows you to appeal to a wide audience while improving the visibility of your content in search engines. By writing for your target audience while incorporating SEO principles, you can communicate effectively and increase your reach.
SEO tips for gender-appropriate language design
To make your web content both gender-appropriate and search engine-optimised, we recommend the following approaches:
- Use gender-appropriate keywords: When selecting your keywords, make sure to include both masculine and feminine as well as gender-neutral forms. This increases the chances of your content being found by a broader target group.
- Make meta descriptions inclusive: Your meta descriptions should not only contain the relevant keywords, but also be written in gender-inclusive language. This signals inclusivity and increases the relevance of your website.
- Show diversity in images and videos: Make sure that the visual elements on your website, such as images and videos, reflect gender diversity. This not only contributes to an inclusive presentation, but also improves the user experience.
Synergy between gender-sensitive language and SEO
Although gender-inclusive language and SEO may not seem to harmonise perfectly at first glance, they are by no means incompatible. With targeted know-how and strategic planning, you can optimise your content so that it is both inclusive and effective for search engines. This promotes a non-discriminatory online world and contributes to your success. As gender-neutral language is increasingly used online, Google will also be better able to interpret and incorporate it.
At ONELINE, we are happy to support you as an SEO agency in making your web presence both gender-appropriate and SEO-optimised. Contact us for a no-obligation consultation and let’s work together to strengthen and diversify your online presence!