As specialists for web development, SEO, web design and online marketing, this question is one of the most important topics in the daily work at ONELINE. Because we develop web solutions for clients from all sectors. Of course, the various pros and cons of the individual browsers play a decisive role. Therefore, we have compiled the most important information on the advantages and disadvantages of the most common internet browsers today – and give tips on which browser is best suited for whom.
Which are the most popular browsers?
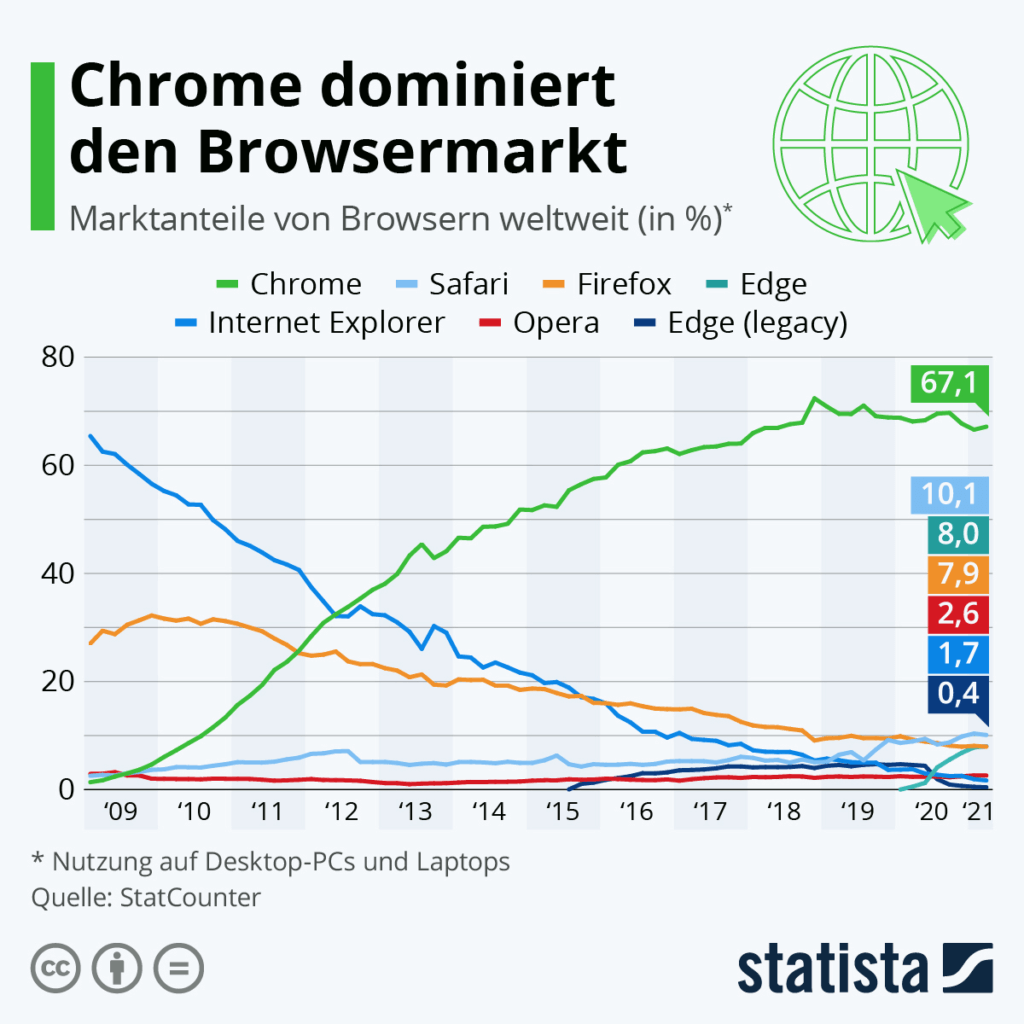
The currently most popular browsers for internet use are Chrome from Google, Firefox from the open source platform Mozilla, Safari from Apple and Edge from Microsoft. Chrome is the undisputed leader by a wide margin. The browsers Brave, Opera and Vivaldi are also widely used. A new variant, DuckDuckGo, is conquering more and more screens.
Chrome and Safari are familiar mainly to users of mobile devices, as these browsers are pre-installed on Android and Apple devices respectively. On desktop computers, on the other hand, either Edge (Windows operating systems) or Safari (Apple PCs) come with them out of the box, depending on the operating system. Since many users use the factory-supplied and pre-installed browsers, the tools mentioned are among the most frequently used applications for web use.
But comparing the different browsers and installing alternative solutions to Edge, Chrome or Safari can really be worthwhile. The range of functions, the speed and the protection of privacy can differ considerably between the different browsers. In web development and web design, our online marketing agency develops homepages, shop systems and social media connections that take into account the strengths and weaknesses of the various web browsers.
What criteria can be used to compare browsers?
In order to compare the pros and cons of the different browsers, comparison factors are important. The most common criteria by which browsers can be measured against each other are:
- Speed
- Extensions
- Privacy protection
- Synchronisation options
- Technical requirements for use
Speed as a comparative factor when choosing a browser
Speed means for an internet browser: How quickly is it ready to start after the programme is called up – and how quickly does it manage to display clicked pages? In terms of start-up speed, Vivaldi is just ahead of Google’s Chrome – whereas competitors like Firefox are rather behind. However, the differences are in the range of seconds.
Browser performance in terms of speed is determined by the respective rendering engine. Google uses its own “Blink” engine, while Firefox uses the “Gecko” engine.
A decisive criterion for the start-up time of a browser is also the use of extensions: The more browser add-ons one uses, the more sluggishly the application starts. Nevertheless, there is much to be said for using a browser with numerous available extensions.
Criterion Browser Extensions in Comparison
All kinds of useful additional functions are hidden under the label “add ons” or “extensions” in a web browser. These include, for example, all kinds of ad blockers. Integrated programmes for better sorting of tabs, for automatic translation of web content and for creating screenshots or recording audio and video content in the browser can also be found among the extensions.
In this comparison criterion, the open source project is clearly ahead among the most popular browsers: Firefox has several hundred extensions, which is the largest number of add-ons in the comparison field.
Privacy protection as a function of a browser
Protecting one’s own data on the internet in the best possible way is becoming increasingly important for more and more users. But many browsers are true data collection machines. Of course, Google, the company behind Chrome, wants to know in as much detail as possible the extent to which a particular user is interested in a particular topic. This way, advertising can be optimally adapted to the user. So from the point of view of an online marketing agency, data collection is definitely desirable.
From the user’s point of view, on the other hand, it is apparent that more and more users value their privacy. In this respect, the individual browsers are suited to very different degrees. While Firefox, for example, is considered relatively exemplary when it comes to protecting user data, Google and Edge can only be recommended to a limited extent in this area. Important to know: As a user, you should know that applying certain privacy settings involves some effort.
For users who are particularly concerned about their privacy, the browsers Brave and DuckDuckGo are recommended. The latter, however, is so far only available as a browser for mobile devices and is characterised by the fact that it neither stores the IP address nor allows cookies or tracks the browsing history.
Comparison regarding synchronisation possibilities
Many modern users use more than one device for surfing, shopping or even working on the internet. In order to have one’s own browser contents, stored access data, bookmarks and histories available in parallel on devices such as PC, laptop, tablet and smartphone, the synchronisation function of the browsers is important.
The good news is that many current browsers offer synchronisation on different devices out of the box. The Edge browser from Microsoft is considered to be particularly far ahead – but you have to have an active Microsoft account to use it.
Importance of technical usage requirements for browser use
Technical requirements for use means: What equipment (software and hardware) must a device have so that the desired browser can run on it at all? Here, most web browsers are characterised by a wide range: They are mostly backwards compatible even in newer versions – so they can usually be used on older devices without any problems.
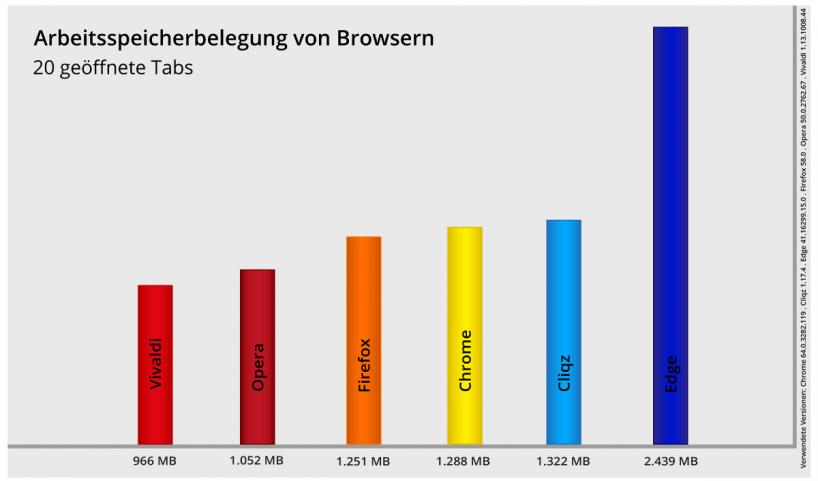
The only outlier is Microsoft’s Edge: this requires a processor power of at least 1 GHz and at least 2 GB RAM for 64-bit systems. This excludes many older systems from using the Edge browser.
Google’s Chrome also makes comparatively high demands. This is because this browser is considered to be particularly RAM-hungry, i.e. it occupies a large part of the working memory. Opera, on the other hand, is considered to be particularly economical with RAM.
The comparison: Chrome, Firefox and Edge
Based on the various criteria presented, the most common web browsers can be classified in terms of their individual strengths and weaknesses.
The advantages and disadvantages of Mozilla’s Firefox
Firefox is considered somewhat cumbersome to start, but convinces with an enormous variety of extensions as well as good privacy protection.
The advantages and disadvantages of Google’s Chrome
Chrome is the undisputed leader of all current web browsers, but it has also been criticised for its tracking functions and high RAM requirements.
The advantages and disadvantages of Microsoft’s Edge
Edge has to contend with prejudices due to the legacy of its predecessor: for many years, Microsoft’s Internet Explorer was regarded as a cumbersome web browser that was severely limited in its functions. With Edge, however, the provider is now doing many things right, which is particularly interesting for users who want good synchronisation across multiple devices.
Other browsers worth recommending
Alternatives such as Brave or DuckDuckGo offer interesting web browsers to all those users who do not want to rely on the established giants such as Chrome, Safari or Firefox. Such alternatives are especially recommended for all friends of the highest possible privacy.
As a general rule, browsers should be chosen according to your own taste, usage preferences and privacy wishes. As a specialist in online marketing, web development, web design and SEO, ONELINE is happy to advise its customers on which browsers their web content should ideally be optimised for.




